Introduction
In the realm of medical curiosities, one question frequently generates intrigue and bewilderment: “Can tonsils grow back after being removed?” The short answer is yes, albeit with certain provisos. In this article, we’ll dive into the depths of tonsil regrowth post-tonsillectomy, dissecting the conditions under which this phenomenon might occur and its implications for health.
Understanding the Tonsillectomy
A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the complete removal of tonsils, the soft tissue masses located at the back of your throat. This procedure is usually conducted to treat chronic tonsillitis, sleep apnea, or other respiratory issues associated with swollen tonsils. However, despite being a common surgical procedure, there’s a chance, albeit slim, of tonsils regrowing post-tonsillectomy.
The Phenomenon of Tonsil Regrowth
The likelihood of tonsil regrowth is primarily tied to the residual tissue left after the surgical procedure. If the surgeon leaves behind some tonsillar tissue during the procedure, there is a possibility that this remaining tissue can regenerate over time, leading to partial tonsil regrowth. It’s important to note, though, that regrowth to their original size is highly unlikely.
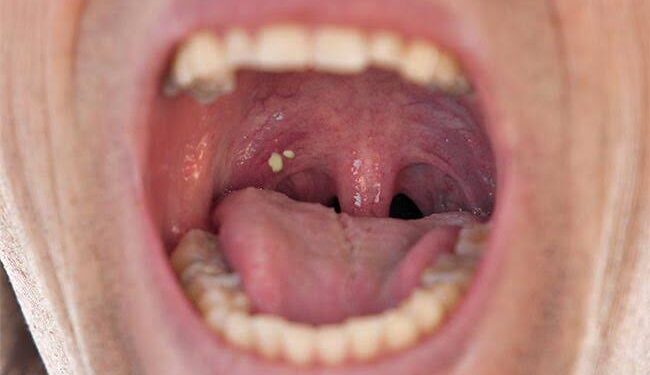
Symptoms and Detection of Tonsil Regrowth
The symptoms of tonsil regrowth are largely the same as those for tonsillitis. The regrowth may present as swollen bumps in the area where the tonsils used to be, causing discomfort, difficulty swallowing, or even a persistent sore throat. If these symptoms appear, especially if they’re coupled with the recurrence of previous conditions such as sleep apnea or chronic infections, it could indicate tonsil regrowth.
A visit to your healthcare provider will provide a definitive diagnosis. A simple physical examination or a throat swab is usually sufficient to confirm whether the tonsils have regrown.
Influencing Factors of Tonsil Regrowth
Certain factors can potentially increase the likelihood of tonsil regrowth. These include the age at which the tonsillectomy was performed (with younger patients having a higher chance), the type of tonsillectomy performed, and the patient’s overall health status, including history of allergies, upper respiratory infections, or a prior history of acute tonsillitis.
Treatment and Management of Tonsil Regrowth
Tonsil regrowth doesn’t always necessitate treatment, especially if it’s not causing any significant discomfort or recurring infections. However, if you’re experiencing persistent issues, medical intervention may be necessary. Treatments would largely mirror those used prior to the tonsillectomy, such as antibiotics for infection or anti-inflammatory medication for swelling.
In rare cases where regrown tonsils cause severe symptoms, another surgical procedure might be recommended. However, it’s important to bear in mind that this is an extreme measure, typically only considered when all other treatment options have failed.
Conclusion: The Rarity of Tonsil Regrowth
Despite the possibility, tonsil regrowth following a tonsillectomy is a relatively rare phenomenon. If you’ve undergone a tonsillectomy, the odds are in your favor that your tonsils will not grow back. However, if you suspect they have regrown, particularly if you’re experiencing familiar symptoms, it’s always prudent to seek medical advice. Although tonsil regrowth can cause some discomfort and concern, it’s typically a manageable condition with proper care and attention.