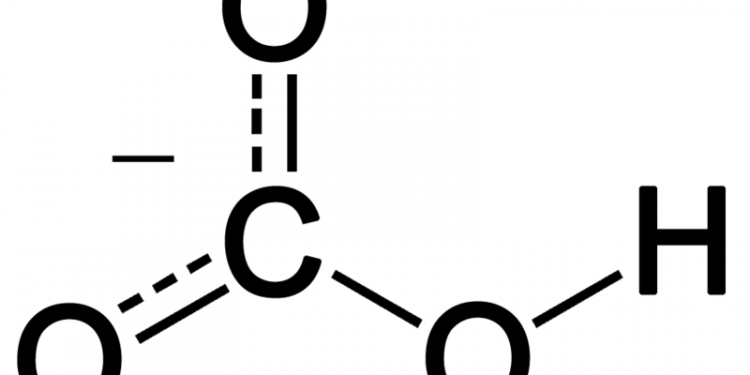
Hydrogen Carbonate
Unlike other carbon compounds, Hydrogen carbonate is nonhazardous and a sink for the carbon cycle. It is used in baking and as an acidity regulator. Also it is a nonhazardous leavening agent. It is a polyatomic anion. Also it is produced during the deprotonation of carbonic acid. Read on to learn more about this element. Then, decide whether or not it’s right for you.
Bicarbonate is a sink in the carbon cycle
The dominant dissolved form of carbon in sea water and most fresh waters is bicarbonate. It is an important sink in the carbon cycle. During periods of high photosynthetic activity, the ocean releases gaseous oxygen and produces bicarbonate ions that shift the pH of water upward. However, high pH can be toxic for many organisms and the high alkalinity causes other chemical constituents to become toxic. In contrast, low photosynthesis results in a rapid drop in pH levels.
The carbon cycle involves the exchange of carbon between the biosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere of the Earth. This exchange results in a global carbon budget that represents the balance of the carbon fluxes between the three reservoirs. One of the key concepts to understand the carbon cycle is how this carbon moves from source to sink. The concept of sinks is important because of how important it is in mitigating the effects of increased CO2 emissions.
There are two main greenhouse gases involved in the carbon cycle. CO2 is the main constituent of the atmosphere. During the pre-industrial period, the atmospheric CO2 concentration remained relatively stable. It is believed that the pre-industrial carbon cycle consisted of a 0.6 gigatons per year ocean release. Bicarbonate is a sink in the carbon cycle. In this process, carbon dioxide reacts with water in solution and forms bicarbonate and hydrogen ions.
On the other hand, the lithosphere is an important source of carbon. It contains more carbon than any other material on Earth. The carbon is stored there in rocks and sedimentary lands than in the atmosphere. These rocks are called limestones and contain high levels of calcium carbonate. A large amount of the carbon that enters the atmosphere is stored in these deposits. Therefore, bicarbonate is an important part of the carbon cycle.
It is a leavening agent
Leavening agents are compounds that cause doughs and batters to expand. These leavening agents include air, steam, and baking powder. They produce carbon dioxide gas through a chemical reaction. These leavening agents are used in baked goods like cookies, cakes, and quick breads. The most common type of leavening agent is sodium bicarbonate, which is a white crystalline substance that is ground into a fine powder for baking. When baking soda is added to flour, it produces carbon dioxide gas. Air is also used in pastry, but it doesn’t produce carbon dioxide.
Sodium bicarbonate is a white crystalline compound that is soluble in water. This substance is also used in fire extinguishers. It is a natural leavening agent and can absorb odors. Sodium bicarbonate is also a common ingredient in toothpaste and tortilla products. This substance can also be used in combination with other leavening agents to produce the desired effect.
Another popular form of sodium bicarbonate is baking soda, which is a neutralizing agent for a variety of foods. This substance reacts with a wide range of acidic materials to produce CO2. Baking soda is often used to balance the leavening in chocolate cakes to avoid the Dutch cocoa effect. However, a side effect of sodium bicarbonate is the soapy aftertaste it can leave on the mouth.
There are different kinds of sodium acid pyrophosphates (SAPPs), which react with hydrogen carbonate at varying temperatures. The higher the temperature, the slower the ROR will be. The slower the ROR, the coarser the cell structure will be. These differences are important when comparing baking soda products. However, a combination of the two is preferred for the most consistent leavening in baked goods.
It is an acidity regulator
Hydrogen carbonate is a common additive used to preserve food and as an acidity regulator. It also helps preserve food by preventing it from absorbing moisture from the air. It also keeps frozen foods fresh by preventing them from melting in storage. While it’s often used as an acidity regulator, hydrogen carbonate can be beneficial in other applications. Here are some examples. In addition to its usefulness as an acidity regulator, hydrogen carbonate is also an effective dehydrator.
The most common form of hydrogen carbonate is sodium bicarbonate. Other names include sodium acid carbonate and sodium carbonate. The suffixes acid and bicarbonate indicate sodium and carbon dioxide, respectively. In addition to its acidity-regulating qualities, hydrogen carbonate is also used as a leavening agent. It is used in baking soda and in the production of baking powder. It can neutralize acids and neutralize pH levels in foods and is also used in toothpaste.
Acidity regulators are organic acids or mineral bases. These compounds are used to control the pH levels of food. They are also used as buffers and neutralizing agents. The first acidity regulator was isolated in 1780 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Known as milk acid, it plays an important role in biochemical processes. It is also a precursor to nylon. It is a white, crystalline substance.
Sodium bicarbonate is another common acidity regulator. It is a monopotassium salt of carbonic acid and has antifungal properties. It’s often used in organic farming to control powdery mildew. It can also be used as a food additive. It is soluble in water and has a slight salty taste. In addition to its acidity-regulating functions, potassium hydrogen carbonate is used as an additive in winemaking. It also acts as a buffer in medications and is used as a fungicide.
It is nonhazardous
Hydrogen carbonate is a common chemical compound. It is found in nature, and is the metabolite of the bacteria Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli, and mouse. Hydrogen carbonate is a carbon oxoanion and the conjugate base of carbonic acid and carbonate. When it is used in biological experiments, it is useful as a biosensor of acid-base physiology.
The EPA classifies Hydrogen carbonate as nonhazardous waste if it meets certain criteria. Its CAS number is 144-55-8. It is listed in the TSCA inventory, but not in the Chemical Test Rule or the Health and Safety Reporting List. In addition, none of the chemicals in the substance are TSCA section 12b or SNUR, and it does not fall under the RQ or TPQ categories.
It is used in fuel cells
Fuel cells are energy-producing devices that use an electrolyte of hydrogen and carbon monoxide to produce electricity and high-quality heat. Hydrogen carbonate is a common fuel in fuel cells and is used in both electric cars and alternative energy sources. Hydrogen and carbon monoxide react with oxygen in the air to produce carbon dioxide and water. These gases are both released as waste by a fuel cell.
This kind of fuel cell differs from the ones discussed so far in that it utilizes a mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen that is generated by the combustion of water or fossil fuel. It uses molten potassium lithium carbonate in the electrolyte. This type of fuel cell must be heated to 650 degrees Celsius and will take several hours to reach operating temperature. The fuel cell is typically made of special engineering plastics and metals.
Fuel cells that use molten carbonate do not generate carbon monoxide, but they can use other forms of fuel such as coal. Molten carbonate fuel cells are generally used in large stationary power plants, although consumers could benefit from them as well. These fuel cells also allow for the reuse of waste heat, which is usually used for industrial processing or space heating. In many cases, this waste heat is even used to generate electricity.
The carbonate eutectic is a common fuel in DCFCs. Carbonate-based DCFCs have several configurations, but the Na-K carbonate eutectic showed the worst performance in fuel cells. The Na-K carbonate eutectic is an example of a fuel cell with a high melting point. Using Na-K carbonate as a fuel cell is an alternative fuel for vehicles.